Reading time: 6 min

There are many techniques for customizing your merchandise or promotional items.
How to know which one is best suited for your needs?
Each technique has its advantages and disadvantages, it's crucial to understand them well to make the best choice. Whether you want to make a short series of very colorful t-shirts or a large series of t-shirts with a single-color design, there is always a more suitable solution that will allow you to optimize the cost of your merch.
To help you choose, we will present machine embroidery, screen printing, digital printing, screen transfer, and pad printing.
Machine embroidery
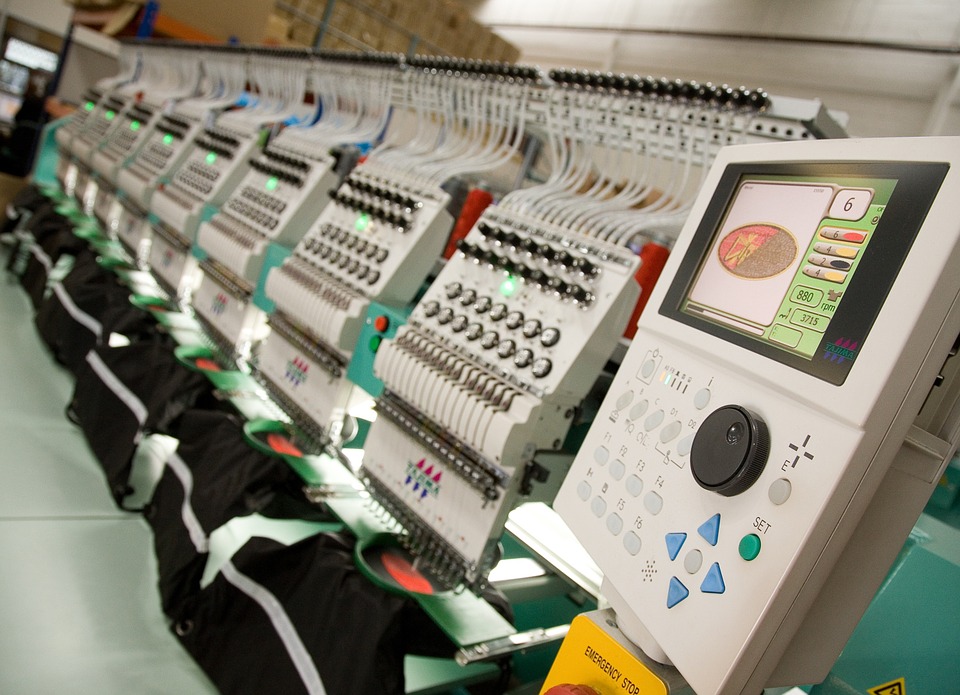

Embroidery is one of the first computer-aided manufacturing techniques. It is considered the most noble and high-end textile marking technique with its relief, pleasant feel, robustness, and durability. Obviously, this superior quality requires a higher price than other techniques like screen printing. You can choose a design with as many colors as you want without affecting the price, but it's important to know that gradients can't be achieved. It's the size of the area to be embroidered that determines its cost, whether higher or lower. That's why we use it for patches, caps, and polo shirts.
The technical part: The machine is controlled by a computer and has a system that keeps the area to be embroidered taut. The computer automatically moves this area according to the programmed design.
Screen printing
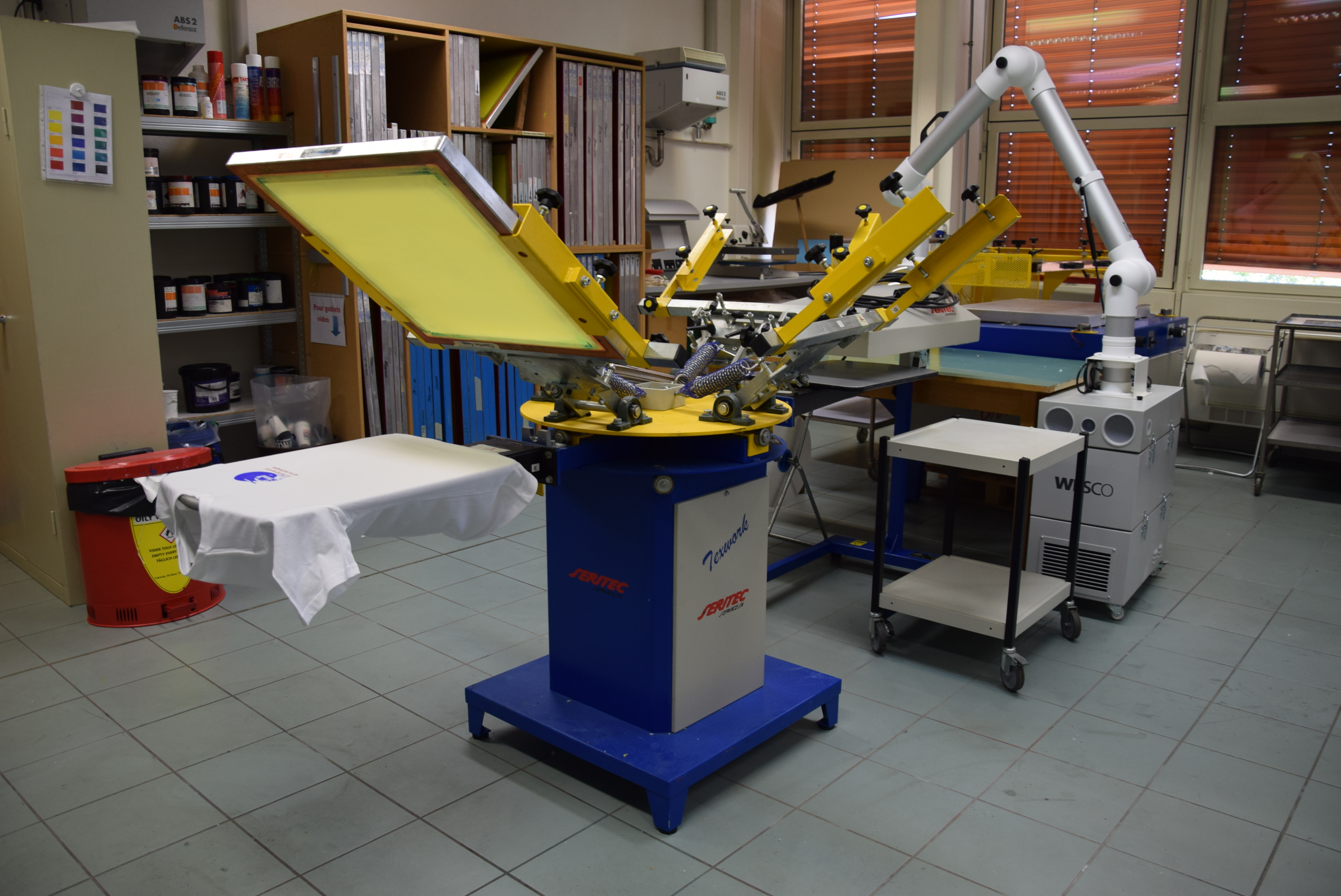

Screen printing is one of the oldest textile marking techniques derived from stenciling that we use for customizing t-shirts, sweatshirts, patches and tote bags. It involves printing a design by superimposing layers of color, so the more colors in the design, the higher the cost. It's therefore one of the most cost-effective techniques for large series with designs using few colors while maintaining impeccable quality and a pleasant touch. Another constraint to consider is that to set the color, the ink must be exposed to a high temperature, so it's advisable to use this technique only on textiles composed mainly of cotton.
If you want more information about the screen printing process, you can find more in our article: The must-have of merchandising: textiles.
Direct to garment (DTG) or digital printing
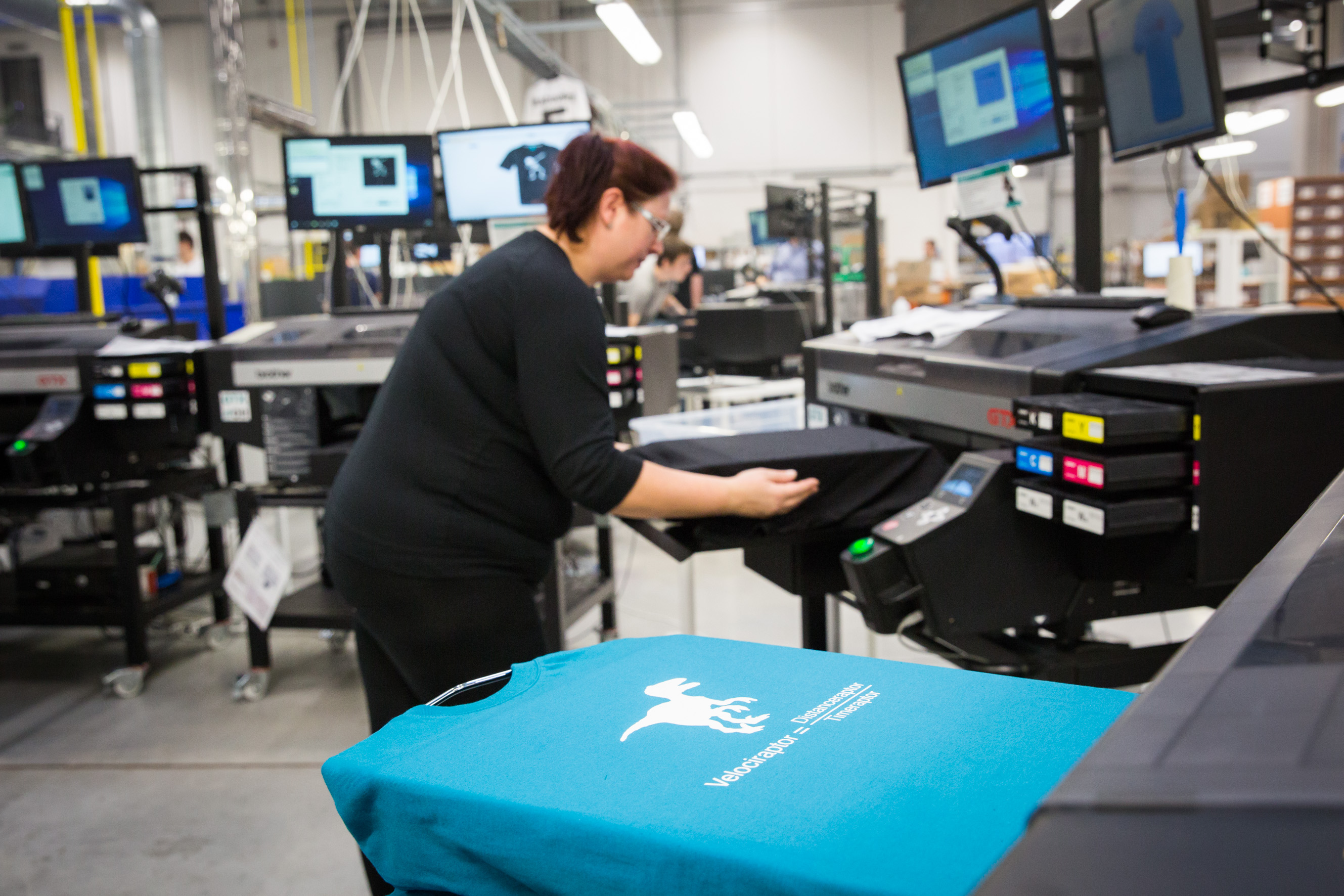

Digital printing is the most recent technique. The design is printed directly onto the t-shirt with a high-definition inkjet printer. The ink absorbed by the fabric leaves a smooth, uniform, and matte impression. For dark fabrics, a white undercoat is first printed to preserve the brightness of the colors. This constraint means that direct printing is more expensive on dark fabrics. This technique is only suitable for fabrics composed of at least 70% cotton. It allows printing detailed, precise, and realistic colored designs with gradients but is more cost-effective for smaller series.
Screen transfer
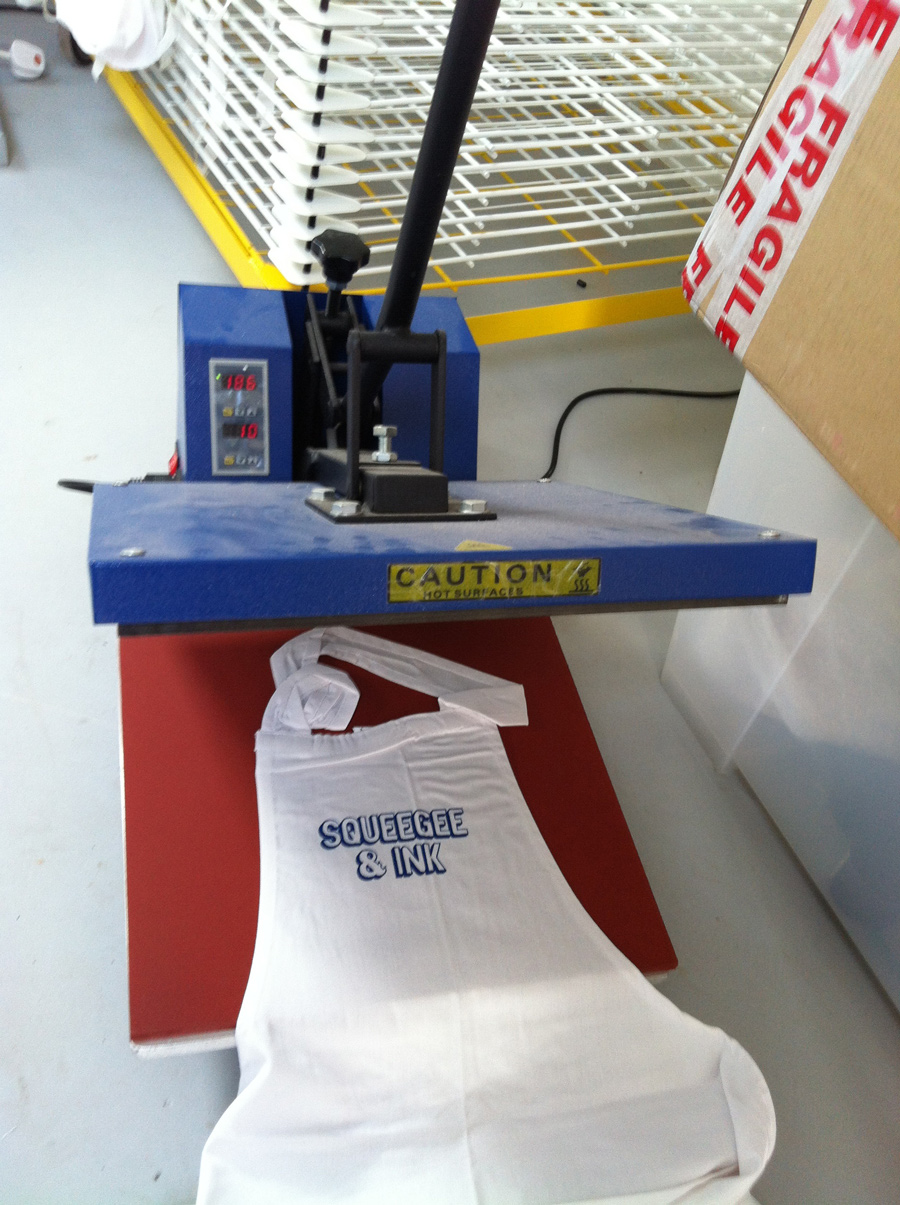

Screen transfer is a mix between the classic transfer technique, which is more mainstream and thus less qualitative, and screen printing. It involves screen printing a transfer sheet and heat-pressing it onto a garment, regardless of its material, leaving a thin, pleasant-to-touch design. The fabric color doesn't affect the transfer cost since the design is adhered to it, however, the number of colors in the design does influence the cost as the sheet is screen printed. Since the fabric isn't impregnated with ink, the marking is less durable in the long term than classic screen printing. Screen transfer is therefore less cost-effective for large series as it requires screen printing transfer sheets one by one, which then need to be adhered to the t-shirt, adding an extra step in the t-shirt customization process compared to screen printing. The result, however, is always of good quality, with fine details and impeccable contours.
Pad printing
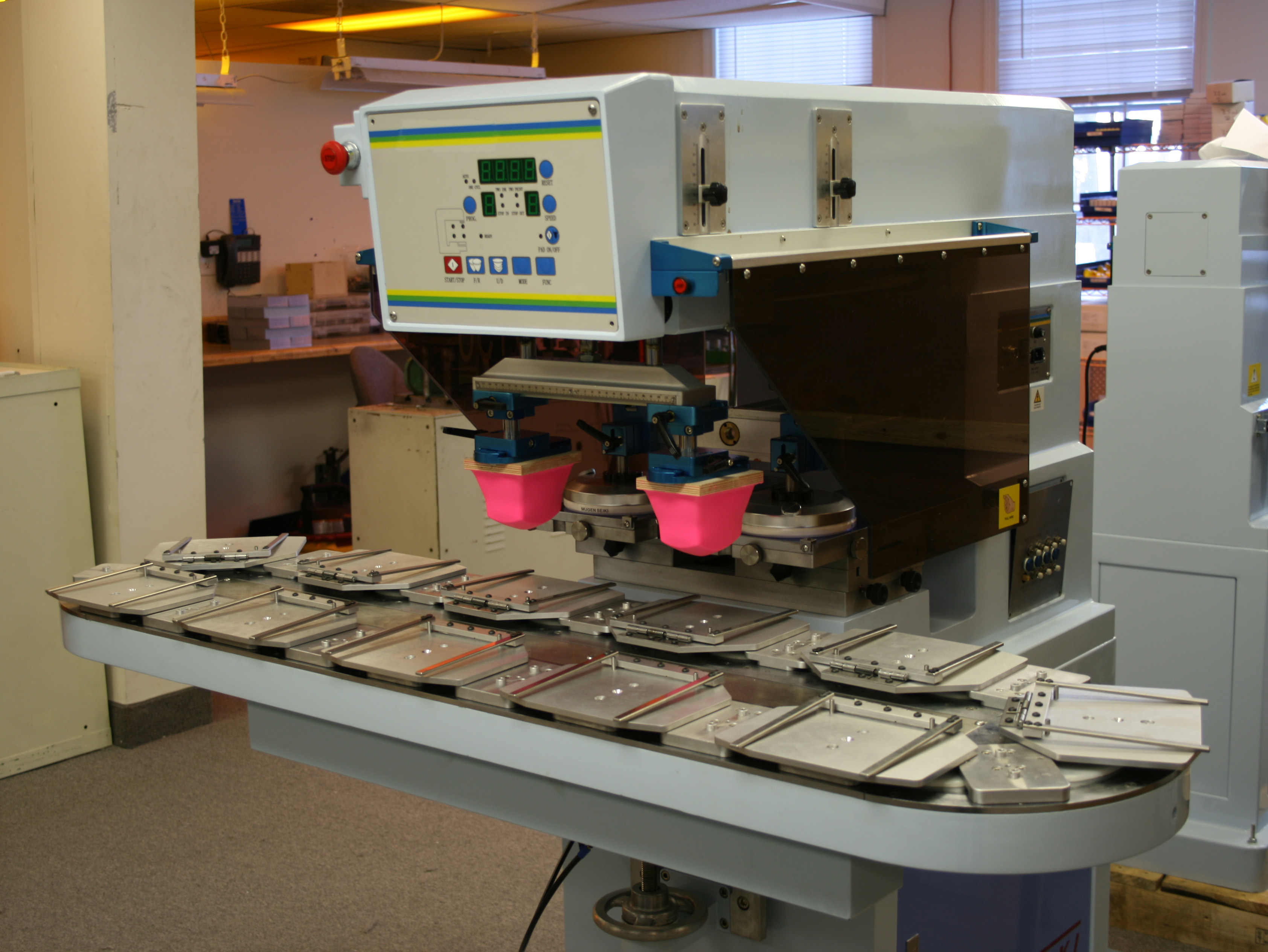

Pad printing is the preferred customization technique for promotional items. Indeed, it allows marking any type of material using a pad quickly and at low cost, whether for large or small series. However, it has some constraints. It is not recommended to pad print flexible or textile materials. As this technique is not the most precise, it is not the most suitable for halftones or marking designs with multiple colors.
Some technical details: The pad leaves a thin layer of ink. This ink takes more or less time to dry depending on the material. It is not recommended to put pad-printed promotional items in the dishwasher as it may alter the design.
In summary
Here's a summary table to help you understand the difference between each marking technique. Don't hesitate to consult it before placing an order to ensure you make the most suitable choice. In any case, at Distrolution Merch, we always advise you before starting production to ensure you're completely satisfied with your order. If you want to share these tips with your friends, don't hesitate to share this article on social media!
| Customization techniques | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Embroidery |
High-end Pleasant to touch Robust |
Higher price Cannot be done on all types of materials Does not allow for gradients |
| Screen printing |
Economical for large series with one or two colors Pleasant touch Durable |
The more colors, the higher the cost Expensive for small series Especially suitable for 100% cotton products |
| Digital printing |
Very smooth touch, no relief Cost-effective for designs with shades Allows printing of gradients Suitable for small series |
Higher price than screen printing, especially for large designs Higher price for dark textiles |
| Screen transfer |
Allows marking different types of materials (cotton, polyester) No additional cost for dark textiles Thin layer, therefore pleasant to touch |
Higher cost depending on the number of colors Less durable than screen printing Higher cost than screen printing for large quantities |
| Pad printing |
Preferred technique for promotional items Perfect for single-color designs Fast and economical |
Not suitable for textiles Monochrome marking Not recommended for flexible objects |








